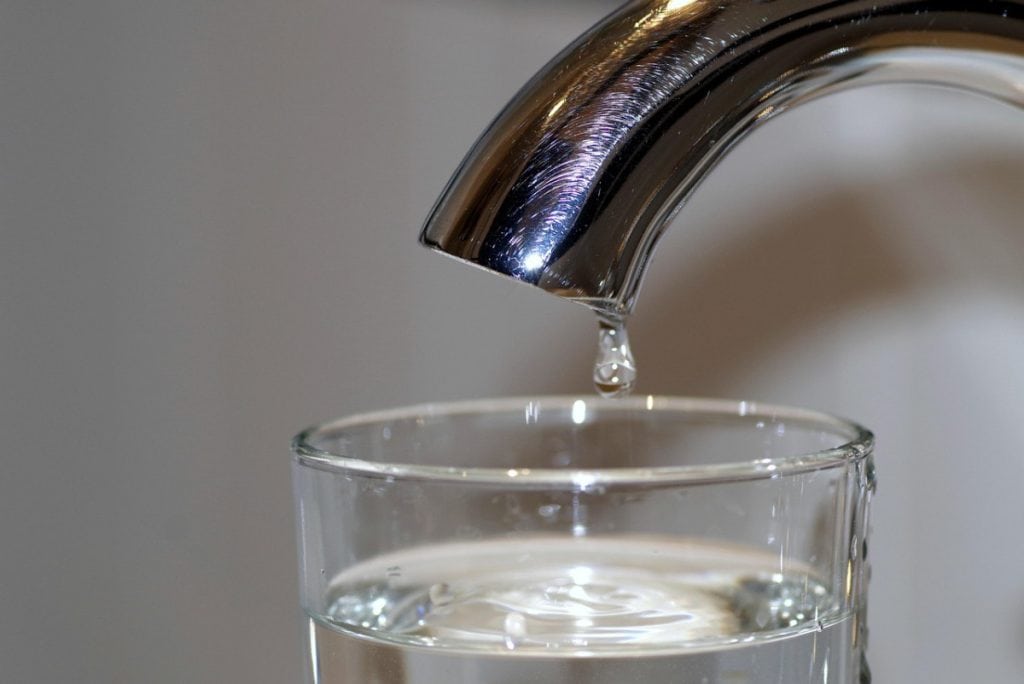
How to Troubleshoot a Water Heater That Won’t Heat Water
Water heaters are essential appliances in our homes, providing hot water for showers, dishwashing, and laundry. When a…
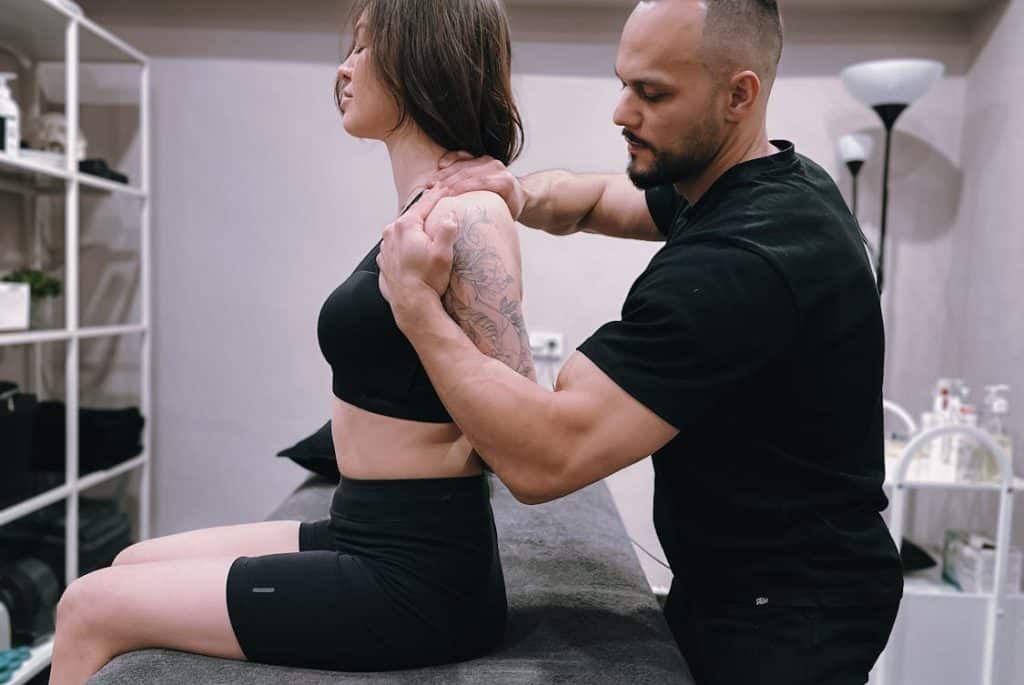
How Chiropractic Therapy Can Improve Your Posture
Posture refers to the alignment of your body while standing, sitting, or lying down. Good posture maintains the…
How Plumbing Problems Could Lead to Serious Health Hazards
Plumbing issues like clogged drains, leaky pipes and running toilets are annoying enough but they can also be…
Why Skipping Epoxy Coating Could Cost You Thousands
Epoxy coating can take anywhere from a few days to a full week to fully cure. During this…
What Makes a Successful AI Model Training Process? Find Out
Training AI models requires heavy volumes of data that contain appropriate diversity and granularity. Teams also face significant…
Is an Epoxy Flooring Worth It? The Answer May Surprise You
A wide variety of epoxy floor coatings exist that offer different performance and aesthetic characteristics. Depending on environmental…
Strategic Electrical Estimating: Professional Standards
Electrical estimators must have access to reliable tools and resources to do their jobs well. These include national…
Why Doing Business in California Has Become So Hard
California’s business landscape presents a complex mix of opportunities and challenges. The state’s economy, known for innovation and…
How to Budget for Your Garage Floor Renovation: Expert Tips
In the midst of a cost-of-living crisis, homeowners have been focusing on ways to improve their homes without…
The Dockworkers Port Strike Shows How Vulnerable Our Economy is
The strike stemmed from ongoing contract negotiations between the International Longshoremen’s Association and the United States Maritime Alliance.…
Understanding the Value of Specialized Consulting Expertise
Understanding the Value of Specialized Consulting Expertise Specialized consulting expertise is a powerful way to boost your firm’s…
Arizona Business Sales: What Buyers Need to Know in 2024
Florida offers a warm climate and job opportunities, making it an attractive property investment market. However, securing financing…
Transform Your Space with Modern Epoxy Floor Designs
Transform your space with modern epoxy floor designs that are both stylish and functional. From bold statement colors…
What Happened to Quiznos Subs: The Decline of a Once-Popular Sandwich Chain
Quiznos, once a major player in the fast-food sandwich industry, has experienced a dramatic decline in recent years.…
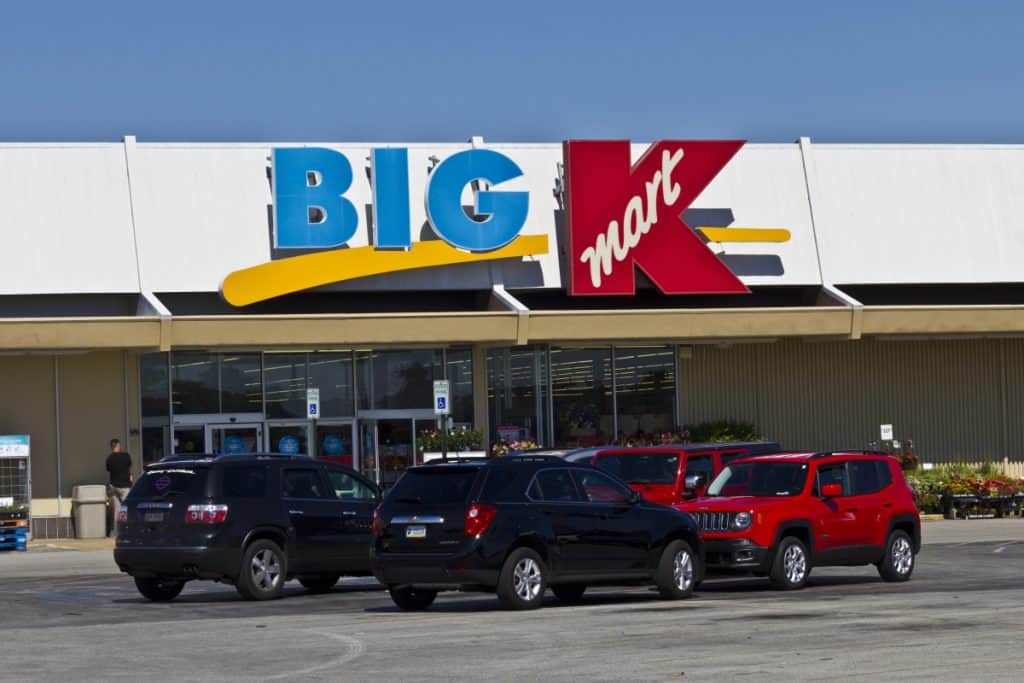
Whatever Happened to Kmart: The Decline of a Retail Giant
Kmart’s journey from a single store to a retail giant spans several decades. The company’s rise and fall…
Professional Electrical Services for Modern Auckland Businesses
Commercial electrical services provide the power to keep businesses running and energised. Their expertise supports productivity and efficiency.…
Professional Property Surveys: A Comprehensive London Guide
Purchasing a property is a significant undertaking, and it’s important to be fully prepared. A property survey is…
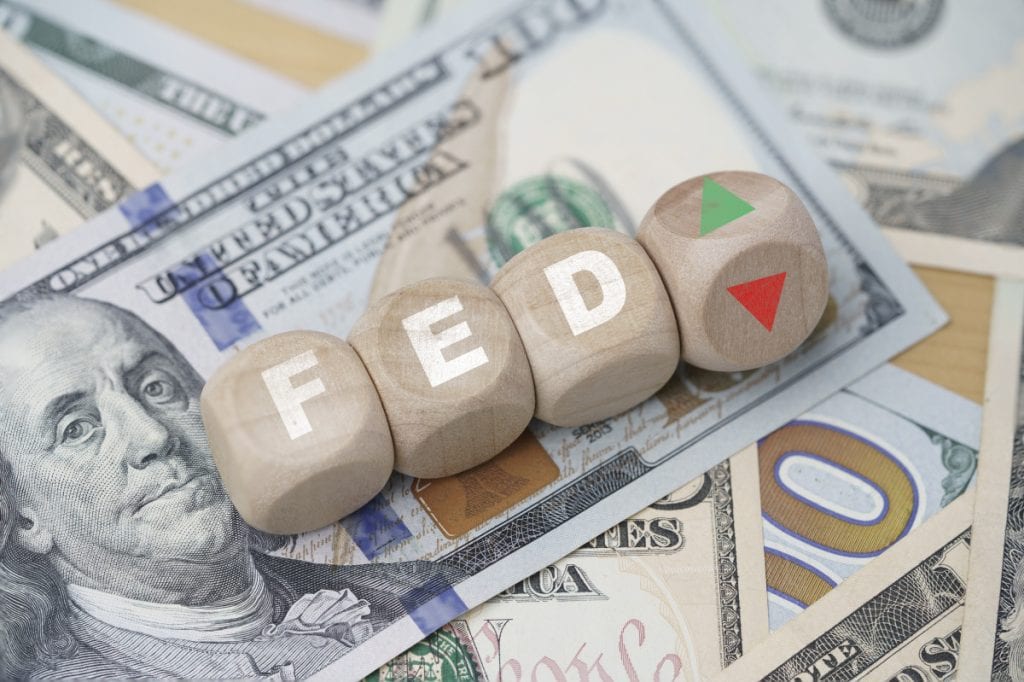
Inflation, Fed Rate Cut: What’s Next for Your Wallet?
The Fed just made a big move. They cut interest rates for the first time in four years.…
4 Principal Advantages of AI in Medical Information Management
Using AI to optimize data analytics enhances diagnostic accuracy and supports better clinical outcomes. It also helps reduce…
Juice Therapy Myths: Separating Fact from Fiction
Juice therapy is all the rage these days, but does drinking fruit and vegetable juice for days or…
Trending Posts
How to Troubleshoot a Water Heater That Won’t Heat Water
Water heaters are essential appliances in our homes, providing hot water for showers, dishwashing, and laundry. When a…
How Chiropractic Therapy Can Improve Your Posture
Posture refers to the alignment of your body while standing, sitting, or lying down. Good posture maintains the…
How Plumbing Problems Could Lead to Serious Health Hazards
Plumbing issues like clogged drains, leaky pipes and running toilets are annoying enough but they can also be…
Why Skipping Epoxy Coating Could Cost You Thousands
Epoxy coating can take anywhere from a few days to a full week to fully cure. During this…
What Makes a Successful AI Model Training Process? Find Out
Training AI models requires heavy volumes of data that contain appropriate diversity and granularity. Teams also face significant…
Is an Epoxy Flooring Worth It? The Answer May Surprise You
A wide variety of epoxy floor coatings exist that offer different performance and aesthetic characteristics. Depending on environmental…
Strategic Electrical Estimating: Professional Standards
Electrical estimators must have access to reliable tools and resources to do their jobs well. These include national…
Why Doing Business in California Has Become So Hard
California’s business landscape presents a complex mix of opportunities and challenges. The state’s economy, known for innovation and…
How to Budget for Your Garage Floor Renovation: Expert Tips
In the midst of a cost-of-living crisis, homeowners have been focusing on ways to improve their homes without…
The Dockworkers Port Strike Shows How Vulnerable Our Economy is
The strike stemmed from ongoing contract negotiations between the International Longshoremen’s Association and the United States Maritime Alliance.…
Top Weekly Inspiration
How to Troubleshoot a Water Heater That Won’t Heat Water
Water heaters are essential appliances in our homes, providing hot water for showers, dishwashing, and laundry. When a…
How Chiropractic Therapy Can Improve Your Posture
Posture refers to the alignment of your body while standing, sitting, or lying down. Good posture maintains the…
How Plumbing Problems Could Lead to Serious Health Hazards
Plumbing issues like clogged drains, leaky pipes and running toilets are annoying enough but they can also be…
Why Skipping Epoxy Coating Could Cost You Thousands
Epoxy coating can take anywhere from a few days to a full week to fully cure. During this…
What Makes a Successful AI Model Training Process? Find Out
Training AI models requires heavy volumes of data that contain appropriate diversity and granularity. Teams also face significant…
Is an Epoxy Flooring Worth It? The Answer May Surprise You
A wide variety of epoxy floor coatings exist that offer different performance and aesthetic characteristics. Depending on environmental…
Strategic Electrical Estimating: Professional Standards
Electrical estimators must have access to reliable tools and resources to do their jobs well. These include national…
Why Doing Business in California Has Become So Hard
California’s business landscape presents a complex mix of opportunities and challenges. The state’s economy, known for innovation and…
How to Budget for Your Garage Floor Renovation: Expert Tips
In the midst of a cost-of-living crisis, homeowners have been focusing on ways to improve their homes without…
The Dockworkers Port Strike Shows How Vulnerable Our Economy is
The strike stemmed from ongoing contract negotiations between the International Longshoremen’s Association and the United States Maritime Alliance.…
Aenean Eleifend
6
Posts
AI in Business
4
Posts
Aliquam
3
Posts
Big Tech
6
Posts
u003cemu003eSmall Spaceu003c/emu003e
How to Troubleshoot a Water Heater That Won’t Heat Water
Water heaters are essential appliances in our homes, providing hot water for showers, dishwashing, and laundry. When a…
How Chiropractic Therapy Can Improve Your Posture
Posture refers to the alignment of your body while standing, sitting, or lying down. Good posture maintains the…
How Plumbing Problems Could Lead to Serious Health Hazards
Plumbing issues like clogged drains, leaky pipes and running toilets are annoying enough but they can also be…
Why Skipping Epoxy Coating Could Cost You Thousands
Epoxy coating can take anywhere from a few days to a full week to fully cure. During this…
What Makes a Successful AI Model Training Process? Find Out
Training AI models requires heavy volumes of data that contain appropriate diversity and granularity. Teams also face significant…
Is an Epoxy Flooring Worth It? The Answer May Surprise You
A wide variety of epoxy floor coatings exist that offer different performance and aesthetic characteristics. Depending on environmental…
Strategic Electrical Estimating: Professional Standards
Electrical estimators must have access to reliable tools and resources to do their jobs well. These include national…
Why Doing Business in California Has Become So Hard
California’s business landscape presents a complex mix of opportunities and challenges. The state’s economy, known for innovation and…
How to Budget for Your Garage Floor Renovation: Expert Tips
In the midst of a cost-of-living crisis, homeowners have been focusing on ways to improve their homes without…
The Dockworkers Port Strike Shows How Vulnerable Our Economy is
The strike stemmed from ongoing contract negotiations between the International Longshoremen’s Association and the United States Maritime Alliance.…
Designer’s Home Tours
How to Troubleshoot a Water Heater That Won’t Heat Water
Water heaters are essential appliances in our homes, providing hot water for showers, dishwashing, and laundry. When a…
How Chiropractic Therapy Can Improve Your Posture
Posture refers to the alignment of your body while standing, sitting, or lying down. Good posture maintains the…
How Plumbing Problems Could Lead to Serious Health Hazards
Plumbing issues like clogged drains, leaky pipes and running toilets are annoying enough but they can also be…
Why Skipping Epoxy Coating Could Cost You Thousands
Epoxy coating can take anywhere from a few days to a full week to fully cure. During this…
What Makes a Successful AI Model Training Process? Find Out
Training AI models requires heavy volumes of data that contain appropriate diversity and granularity. Teams also face significant…
Is an Epoxy Flooring Worth It? The Answer May Surprise You
A wide variety of epoxy floor coatings exist that offer different performance and aesthetic characteristics. Depending on environmental…
Strategic Electrical Estimating: Professional Standards
Electrical estimators must have access to reliable tools and resources to do their jobs well. These include national…
Why Doing Business in California Has Become So Hard
California’s business landscape presents a complex mix of opportunities and challenges. The state’s economy, known for innovation and…
How to Budget for Your Garage Floor Renovation: Expert Tips
In the midst of a cost-of-living crisis, homeowners have been focusing on ways to improve their homes without…
The Dockworkers Port Strike Shows How Vulnerable Our Economy is
The strike stemmed from ongoing contract negotiations between the International Longshoremen’s Association and the United States Maritime Alliance.…
How to Troubleshoot a Water Heater That Won’t Heat Water
Water heaters are essential appliances in our homes, providing hot water for showers, dishwashing, and laundry. When a…
How Chiropractic Therapy Can Improve Your Posture
Posture refers to the alignment of your body while standing, sitting, or lying down. Good posture maintains the…
How Plumbing Problems Could Lead to Serious Health Hazards
Plumbing issues like clogged drains, leaky pipes and running toilets are annoying enough but they can also be…
Why Skipping Epoxy Coating Could Cost You Thousands
Epoxy coating can take anywhere from a few days to a full week to fully cure. During this…
What Makes a Successful AI Model Training Process? Find Out
Training AI models requires heavy volumes of data that contain appropriate diversity and granularity. Teams also face significant…
Is an Epoxy Flooring Worth It? The Answer May Surprise You
A wide variety of epoxy floor coatings exist that offer different performance and aesthetic characteristics. Depending on environmental…
Strategic Electrical Estimating: Professional Standards
Electrical estimators must have access to reliable tools and resources to do their jobs well. These include national…
Why Doing Business in California Has Become So Hard
California’s business landscape presents a complex mix of opportunities and challenges. The state’s economy, known for innovation and…
How to Budget for Your Garage Floor Renovation: Expert Tips
In the midst of a cost-of-living crisis, homeowners have been focusing on ways to improve their homes without…
The Dockworkers Port Strike Shows How Vulnerable Our Economy is
The strike stemmed from ongoing contract negotiations between the International Longshoremen’s Association and the United States Maritime Alliance.…
Sign Up for
Our Newsletter
Get notified of the best deals on our WordPress themes.
Follow Us on
Social Media
Recent Design Ideas
How to Troubleshoot a Water Heater That Won’t Heat Water
Water heaters are essential appliances in our homes, providing hot water for showers, dishwashing, and laundry. When a…
How Chiropractic Therapy Can Improve Your Posture
Posture refers to the alignment of your body while standing, sitting, or lying down. Good posture maintains the…
How Plumbing Problems Could Lead to Serious Health Hazards
Plumbing issues like clogged drains, leaky pipes and running toilets are annoying enough but they can also be…
Why Skipping Epoxy Coating Could Cost You Thousands
Epoxy coating can take anywhere from a few days to a full week to fully cure. During this…
What Makes a Successful AI Model Training Process? Find Out
Training AI models requires heavy volumes of data that contain appropriate diversity and granularity. Teams also face significant…
Is an Epoxy Flooring Worth It? The Answer May Surprise You
A wide variety of epoxy floor coatings exist that offer different performance and aesthetic characteristics. Depending on environmental…
Strategic Electrical Estimating: Professional Standards
Electrical estimators must have access to reliable tools and resources to do their jobs well. These include national…
Why Doing Business in California Has Become So Hard
California’s business landscape presents a complex mix of opportunities and challenges. The state’s economy, known for innovation and…
How to Budget for Your Garage Floor Renovation: Expert Tips
In the midst of a cost-of-living crisis, homeowners have been focusing on ways to improve their homes without…
The Dockworkers Port Strike Shows How Vulnerable Our Economy is
The strike stemmed from ongoing contract negotiations between the International Longshoremen’s Association and the United States Maritime Alliance.…